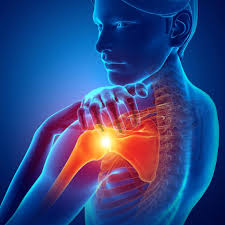
Mencoret.com – Left Shoulder Tendonitis may be a common problem, but there are some steps you can take to reduce your risk of developing this condition. Keeping the right posture is key. Avoid sleeping on your side, and try to keep your arm close to your body. If your pain starts during an activity, try to rest your shoulder. Avoid performing repetitive overhead motions, such as pushing an arm out of a car window.
Surgical procedures should be considered only in extreme cases
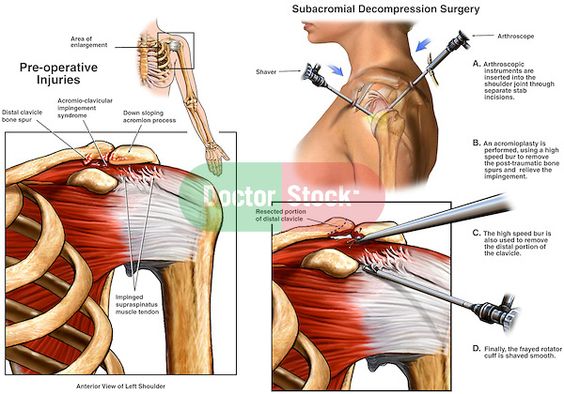
Treatment for shoulder tendonitis may include conservative measures, such as pain-relieving medications, strengthening exercises, or ultrasound therapy. Surgical procedures should only be considered in extreme cases if the condition persists or is chronic. If left untreated, the condition can lead to immobility and chronic pain, which may limit daily activities. Consultation with a physician is essential for proper diagnosis and treatment. In most cases, there is no cure for the disease, but treatment is possible.
Conservative treatment options may include rest and ice packs. Sometimes a surgeon may recommend surgery. Arthroscopy is a common procedure that involves cutting the tendon and removing the calcified deposit. While this procedure can relieve pain and restore mobility, it can also lead to severe tissue damage and a lengthy recovery. Afterward, you’ll need to spend months in a sling and undergo extensive physical therapy.
Early treatment is very important, because pain can greatly affect your lifestyle
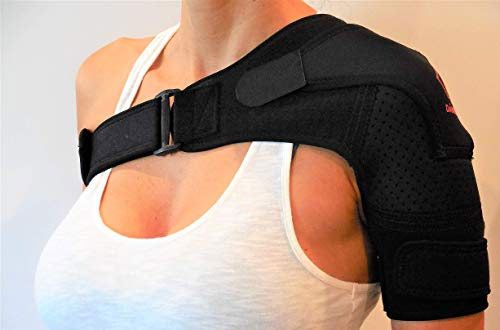
Early treatment is crucial for successful recovery. Fortunately, most cases of tendonitis are treatable. Symptomatic treatments can help minimize pain and restore mobility. Depending on the severity of the injury, surgery may be necessary. Most treatments for tendonitis aim to relieve pain, reduce disability, and prevent recurrence. The early treatment is crucial, as the pain can severely impact an active lifestyle. So, don’t hesitate to consult a doctor if you suspect a shoulder tendonitis.
Acute or chronic condition, tendinitis is caused by inflammation of the rotator cuff tendons. This condition causes pain and stiffness in the shoulder. It can be a result of overuse or general wear and tear. The best treatment for tendinitis involves resting the injured tendon, decreasing inflammation, and correcting imbalances. If left untreated, tendinitis will generally resolve on its own. However, treatment may be necessary if the pain persists.
Bursa is a sac of tissue that lines and protects the shoulder joint
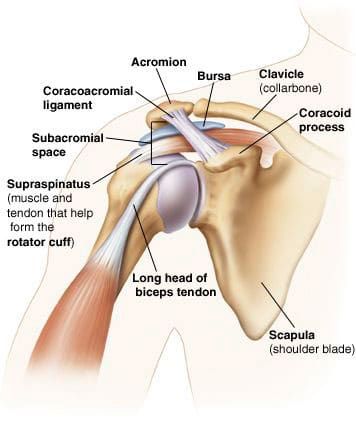
Symptoms of left shoulder tendinitis are often accompanied by AC separation, a partial dislocation of the shoulder joint caused by overuse. This condition can stretch the ligaments that hold the joint in place. Shoulder tendinitis should not be confused with shoulder bursitis. A bursa is a sac of tissue that cushions and protects the shoulder joint. The labrum in this area is extremely fragile and should be checked by a medical professional if it is inflamed.
If you experience pain in your shoulder, visit a doctor immediately. If the pain is accompanied by heaviness or a pressure sensation in your chest, it may be a sign of a heart attack. While shoulder pain typically subsides with time, it can also be caused by a bursitis. For the best results, ice or heat therapy should be applied to the shoulder for several hours daily. It is important to remember that using heat on an injured area may cause frostbite or other complications.
Overuse of these muscles can cause them to get inflamed

Exercises for left shoulder tendonitis include stretches that will reduce pain and inflammation. The muscles and tendons of the shoulder are connected to four rotator cuff tendons. Overuse of these muscles can cause them to become inflamed, stretched, or torn. These injuries are typically caused by trauma or normal wear and tear associated with age. Tenderness in these tendons will increase over time, increasing in severity as your arm gets older.
In the claimant’s case, the Workers Compensation Board adjudicator obtained a sworn statement. The claimant’s hand was dominant in his right arm. He claimed to have had no history of shoulder pain, and his occupation was as a cashier for 20 years. His job involved bagging, scanning, and even boxing. His employer was never aware of the condition, and he also denied him a full recovery.
After surgery, physical therapy will help reduce the pain and inflammation caused by the rotator cuff tendonitis. Physical therapy will allow you to perform a variety of exercises that will help your shoulder heal faster. You can also take nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) if you feel pain and discomfort. If these methods do not work, your doctor may recommend a corticosteroid injection. This procedure is not beneficial, as it is not as effective as physical therapy.