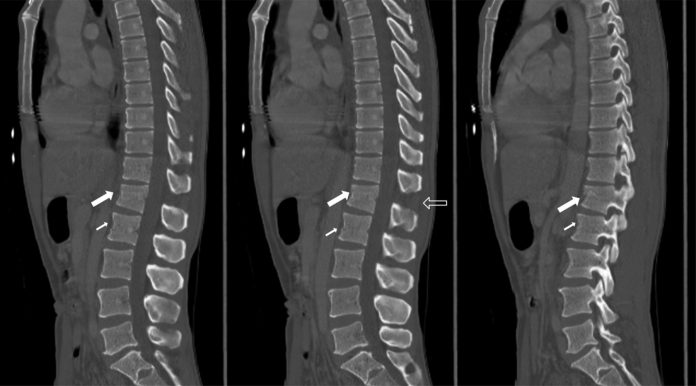
Mencoret.com – Chance fractures are a common type of spinal injury, resulting in the disruption of ligaments and posterior elements. This type of fracture occurs in the thoracolumbar (T10-L2) region, while children may develop the injury in the mid-lumbar area. The fracture line usually proceeds posteriorly through the spinous process and continues through the lamina, pedicles, and vertebral body.
Fractures of the spine are the result of a failed flexion-distraction mechanism
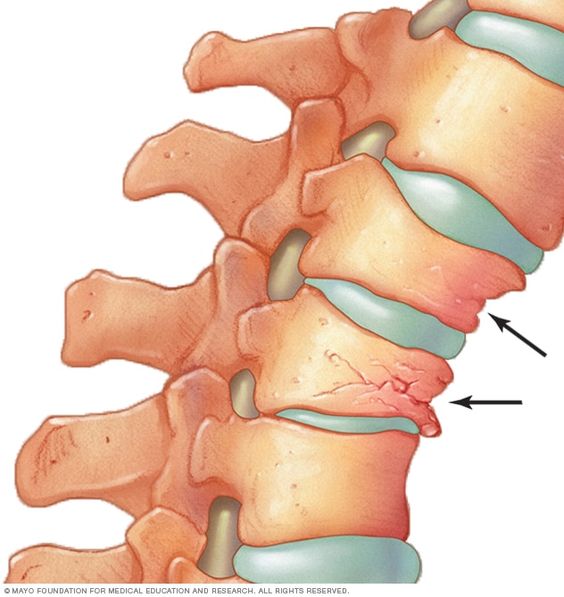
The likelihood of a patient developing a Chance fracture in the spine increases after a car accident. It may also occur when the accident victim fails to wear their seatbelt. A chance fracture of the spine is a result of a flexion-distraction mechanism that fails to properly align a person’s body. It may occur when a vehicle is suddenly decelerating, causing the posterior column of the thoracolumbar spine to fracture anteriorly.
The mechanism of the Chance fracture in this case was different from previous descriptions of this injury. In the event of a rodeo accident, the National Intercollegiate Rodeo Association requires the presence of an ambulance and a team of prehospital care professionals. This allows the injured athlete to receive immediate medical attention. It is also important to note that the mechanism by which a Chance fracture occurs is less important than previously thought. It is also important to understand that there is a wide variety of causes for this type of fracture.
Treatment of Chance’s fracture depends on the extent of the injury

While Chance fractures are not fatal, there is a risk of serious internal organ injuries. These injuries usually affect the duodenum or pancreas, which can result in pain and spine deformity. Treatment of a Chance fracture depends on the extent of the injury. Treatment may include surgery to stabilize the spine. In some cases, it may be necessary to use restraints to prevent further fractures. However, the majority of Chance fractures have a good outcome with proper care.
A thorough neurologic examination is necessary to evaluate the severity of the Chance fracture and identify which vertebrae are at risk for fracture. This information is critical in developing a treatment plan for this condition. The likelihood of surgery is dependent on the degree of neurologic symptoms and the location of the fracture. The Chance fracture treatment option depends on the level of instability. If the patient’s neurological symptoms have progressed, surgery may be necessary.
Posterior spinal distraction signs
Another common symptom of a Chance fracture is the loss of pedicle definition. Five serial transaxial computed tomography images show that the fracture has propagated through the pedicles into the vertebral body. The left-sided portion of the patient’s vertebral body exhibits more loss of pedicle definition. There is no spinous process in the left side, which is a sign of posterior spinal distraction.
In patients with suspected spinal trauma, a computed tomography (CT) study is the best initial imaging study. CT is superior to radiography for detecting fractures. Combined CT scans of the chest, abdomen, pelvis, and spine reveal a variety of injuries, including a Chance fracture. Additionally, a CT scan has coronal and sagittal reformations which are critical for identifying a Chance fracture.
Incidental fractures are frequently associated with neurologic injury
There are two types of Chance fractures. Compression fractures involve the anterior part of the vertebra. The axial burst fracture, a combination of compression and axial distraction, results in a loss of height in both front and back of the vertebra. The chance fracture, on the other hand, involves vertical impact and the pulling apart of the vertebrae. Chance fractures are often associated with neurological injuries.
If the vertebrae slip out of position, the spinal cord is injured. Surgical treatment may be necessary to stabilize the spine and reduce spinal cord compression. In addition, the fracture may be more complicated if neurologic damage or progressive spinal deformity are present. The severity score should be monitored closely and evaluated by a medical professional before surgery is recommended. After the initial surgical procedure, you may have to continue with PT or other rehabilitation therapy until the injury has healed completely.